
1.Main material and structure
Control cables are mainly composed of conductor, insulation, sheath and other parts. The conductor is usually made of highly conductive copper to ensure stable signal transmission. The insulation layer is made of polyvinyl chloride (PVC) and other insulating materials to prevent current leakage and short circuit. The sheath protects the cable from external damage.
2.Performance Characteristics
(1)Transmission performance: Control cables can efficiently and accurately transmit weak electrical signals, such as digital signals, analog signals, pulse signals, etc. These signals are used by automation control systems to achieve precise control. These signals are the basis for automation control system to realize precise control and remote monitoring.
(2)Anti-interference ability: control cables are usually shielded, stranded and other designs to effectively resist electromagnetic interference and radio frequency interference, to ensure the accuracy and stability of signal transmission.
(3)Mechanical properties: control cables have good flexibility and wear resistance, and can adapt to a variety of complex environments and installation conditions.
Safety and reliability: control cables are made of high-quality insulating materials and sheaths, as well as reasonable structural design, to ensure that they can still maintain good electrical performance and mechanical strength in various harsh environments.
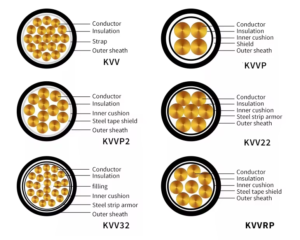
3.Common models and specifications
Control cables are available in a variety of models and specifications to meet the needs of different application scenarios. For example, KVV, KVVP, KVVP2, KVVR, KVVRP and other models represent different insulation materials, shielding methods and sheath types. In terms of specifications, the number of cores of control cables can range from 2 cores to 61 cores, and there are various choices of cross-sectional area.
4.Classification
(1)According to the use can be divided into: power cables, control cables, compensation cables, shielded cables, high temperature cables, computer cables, signal cables, coaxial cables, fire-resistant cables, marine cables, mining cables, aluminum alloy cables and so on.
(2)According to the insulation material can be divided into: oil-impregnated paper insulated power cables, plastic insulated power cables, rubber insulated power cables.
(3)According to the transmission performance can be divided into: coaxial cable, symmetrical cable, fiber optic cable and so on.
Product Applications
1.Industrial automation field
In the field of production line, robot control, automated warehousing, etc., control cables are the key to realize equipment linkage and precise control. They connect all kinds of sensors, actuators and controllers to ensure the stable operation and efficient production of the automation system.
2.Energy and Power Systems
Control cables are used to monitor and manage the generation, transmission and distribution of electrical energy. Inside substations and power plants, control cables are used to protect, measure, and control circuits to ensure stable operation of the grid and quick response to faults.
3.Buildings and infrastructure
In building automation systems (e.g. lighting control, security monitoring, environmental monitoring), control cables connect various types of sensors, actuators and controllers to realize the intelligent control of various devices in the building, and improve the efficiency and comfort of the building. In transportation infrastructure such as highways, bridges, tunnels, etc., control cables also play an important role in ensuring the safety and smooth flow of traffic.
4.Mechanical equipment and instrumentation
Control cables are an integral part of the manufacture of mechanical equipment and instrumentation. They are used to connect various parts of the equipment, transmit control signals and electrical energy, and ensure the normal operation of the equipment. The accuracy and stability of control cables are essential for accurate measurement and control of instrumentation.
5.Communication and network field
In systems such as local area networks and industrial Ethernet, although optical fiber has become the mainstream transmission medium, control cables still play an important role in certain occasions. For example, it is used to transmit low-speed or short-distance data signals for interconnection and communication between devices.
6.Aerospace and Defense
In the aerospace and defense sector, the requirements for control cables are even more stringent. They need to withstand harsh environments such as extreme temperatures, pressure and radiation to ensure the stable operation of aerospace and defense equipment. The confidentiality and reliability of control cables are critical to national security.


© Все права Защищены.